 English name: Cyanuric chloride
English alias: 2,4,6-trichloro-1,3,5-triazine; Cyanuricchloride,98%; TCT; 2,4,6-trichloro-1,2-dihydro-1,2,3-triazine
CAS RN:108-77-0
EINECS:203-614-9
Molecular weight: 184.5
Density: 1.92g/cm3
Melting point: 146 ℃
Boiling point: 194 ℃ Slightly soluble in water
Physical and chemical properties: Crystals with a pungent odor.
Appearance: White crystals
Structural formula: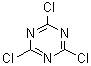
Packaging: Packaged in plastic bags and stored in a cool, ventilated, and dry place. Pay attention to fire prevention, sun protection, and moisture prevention.
Usage: Used for synthesizing fluorescent whitening agents, reactive dyes, pharmaceuticals, pesticides, and other upstream raw materials such as chlorine gas and sodium cyanide
Introduction to Cyanuric Chloride
Cyanuric chloride is an important fine chemical product with a wide range of uses. It is an intermediate in the pesticide industry, a raw material for manufacturing reactive dyes, and can be used as various additives in organic industry production, such as fluorescent whitening agents, textile anti shrink agents, surfactants, etc. It is also one of the raw materials used in rubber accelerators and national defense for manufacturing explosives. It is also a raw material used in the pharmaceutical pesticide industry for synthesizing drugs
Cyanuric chloride (C3N3CL3), also known as cyanuric chloride or cyanuric chloride, appears as a white powder and is unstable in air. It is volatile and irritating, with a melting point of 145.5 ℃ and a relative density of 1.32. It is soluble in organic solvents such as benzene, hot ether, acetone, acetonitrile, dioxane, ethanol, acetic acid, chloroform, and carbon tetrachloride, and is slightly soluble in water. When exposed to water and alkali, it easily decomposes into cyanuric acid and releases hydrogen chloride gas.
Production method
The production of melamine usually consists of two processes: the preparation of melamine and the polymerization of melamine. There are various methods for generating cyanuric acid, such as the synthesis of methyl thiocyanate and chlorine, the synthesis of hydrogen cyanide dissolved in chloroform and introduced into chlorine gas, the hydrogen cyanide method, the sodium cyanide method, the urea method, and the direct chlorination of hydrogen cyanide and chlorine gas. Currently, the industrial production of cyanuric acid
generally uses two methods: sodium cyanide and hydrogen cyanide as raw materials.
1. The sodium cyanide method uses sodium cyanide as raw material to react with chlorine gas to produce cyanuric chloride, which is then polymerized to produce cyanuric chloride. The product is obtained by rapid cooling and crystallization. Raw material consumption quota: 1073kg/t sodium cyanide, 1700kg/t chlorine gas.
2. The hydrogen cyanide method uses hydrogen cyanide as a raw material to react with chlorine gas to produce cyanuric chloride, which is then polymerized to produce cyanuric chloride. The product is obtained by rapid cooling and crystallization. Raw material consumption quota: 500kg/t hydrogen cyanide and 1200kg/t chlorine gas.
Application scope
Cyanuric chloride products have a wide range of industrial applications, with the most commonly used being in the production of herbicides, pesticides, reactive dyes, and fluorescent dyes. There are triazine series herbicides produced using melamine as raw material, such as Chlorpheniramine, Chlorpheniramine, Chlorpheniramine, Ximazin, Xicaozin, Amoxicillin, Atrazine, etc. Pesticides include Dichlorvon.
Used for synthesizing fluorescent whitening agents, reactive dyes, pharmaceuticals, pesticides, etc.
Cyanuric chloride is an important intermediate for the production of efficient and low toxicity triazine herbicides and insecticides, as well as for the production of reactive dyes for various synthetic fibers such as fluorescent whitening agents and polyester. It is also used in the production of synthetic resins, rubber, polymer anti-aging agents, explosives, fabric anti shrink agents, surfactants, and other fields.
|
